Which ports do Omada SDN Controller and Omada Discovery Utility use? (above Controller 5.0.15)
Programs use specific ports to send or receive data via a network. An Omada SDN Controller or Omada Discovery Utility uses the ports on the host, while an Omada hardware controller uses the ports on its hardware.
Ports fall into two groups: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) ports and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) ports. Port numbers are limited, ranging from 1 to 65535 among each group. Such fact gives rise to a port collision when a program tries to use a certain port on a host, only to find the very port is occupied by another program.
From this article, you can learn which ports an Omada SDN Controller (5.0.15 and above) and an Omada Discovery Utility (5.0.8 and above) use, and how to troubleshoot when a port-related problem happens.
An overview of the default ports
The default ports used by the Omada SDN Controller and Omada Discovery Utility are listed in the table below.
|
Ports |
Omada Hardware Controller |
Omada Software Controller |
Omada Discovery Utility |
When the port is required |
|
Web Management and Portal |
||||
|
TCP 80 |
✔ |
|
|
1. When you visit the management page of Omada Hardware Controller via an HTTP connection. |
|
TCP 443 |
✔ |
|
|
1. When you visit the management page of Omada Hardware Controller via an HTTPS connection. |
|
TCP 8088 |
✔ |
✔ |
|
1. When you visit the management page of Omada Software Controller via an HTTP connection. |
|
TCP 8043 |
|
✔ |
|
1. When you visit the management page of Omada Software Controller via an HTTPS connection. |
|
TCP 8843 |
✔ |
✔ |
|
When the clients visit the Portal page via an HTTPS connection. |
|
Device Discovery, Adoption, Management, and Upgrade |
||||
|
UDP 29810 |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
Omada Controller and Omada Discovery Utility discover Omada devices. |
|
TCP 29814 |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
Omada Controller and Omada Discovery Utility manage the Omada devices running firmware fully adapted to Omada Controller v5*. |
|
TCP 29811/29812 |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
Omada Controller and Omada Discovery Utility manage the Omada devices running firmware fully adapted to Omada Controller v4*. |
|
TCP 29813 |
✔ |
✔ |
|
When upgrading the firmware for the Omada devices running firmware fully adapted to Omada Controller v4*. |
|
Initialization Check |
||||
|
UDP 27001 |
✔ |
✔ |
|
Omada Controller can be discovered by the Omada APP within the same network through this port. |
|
Database Access |
||||
|
TCP 27217 |
|
✔ |
|
Omada Software Controller accesses the MongoDB database through this port. |
*New firmware released since 2022 is fully adapted to Omada Controller v5 and upgrades the Omada SDN management protocol. Release notes for new firmware include the following information:

Examples of Omada Controller using ports
In this section, we use the Omada Controller discover devices as an example to explain how the Omada Controller uses ports.
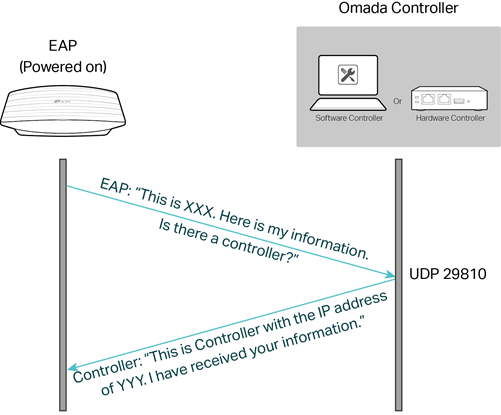
|
Step 1 |
EAP doesn’t know exactly where the controller is, so it broadcasts a self-introductory message to UDP port 29810 in the LAN. |
|
Step 2 |
Omada Controller is listening to the port and receives the EAP introductory message, then replies to the EAP via the same port. |
How to change the port used by Omada SDN Controller?
1. Web Management and Portal Port
Omada SDN Controller supports changing the ports for Web management and Portal via its management page.
Go to Settings -> Controller -> Access Config, there are three ports you can change:
- HTTPS Port for Controller Management,
- HTTPS Port for Portal,
- HTTP Port for Portal.
The modification of the port number will take effect after you restart the Controller.

2. Device Management Port
Omada Software Controller (5.0.15 and above) allows changing the following device management ports by editing the “omada.properties” file. The configuration takes effect after saving the modification and restarting the controller.
For Windows Controller, the default file path is “C:\Users\XXX\Omada Controller\properties” (XXX for your Windows account).
For Linux Controller, the default file path is “/opt/tplink/EAPController/properties”.
It is recommended that you keep the default ports. If you do need to change ports, make sure you do not use duplicate ports or well-known ports. If you change the port for “port.discovery”, you need to use the Omada Discovery Utility to inform the devices of the new controller port.
- port.adopt.v1=29812
- port.upgrade.v1=29813
- port.manager.v1=29811
- port.manager.v2=29814
- port.discovery=29810
For example, there are two Omada Software Controllers in your office to manage the other networks over the Internet. Thus, you should set up port forwarding for these two controllers, but you cannot use the same external WAN ports for them simultaneously. You can modify the ports of one controller and use the corresponding external WAN ports. Here we change the port. discovery to 29820, then run the Omada Discovery Utility and add port 29820 to the Inform URL.

Is this faq useful?
Your feedback helps improve this site.